Cloud Backup Servers – In today’s data-driven world, safeguarding digital information is more critical than ever. The rapid evolution of technology has not only transformed how we store and manage data but also how we protect it. Among the most powerful innovations in this regard is the cloud backup server—a revolutionary solution offering flexible, scalable, and secure data protection. For businesses and individuals alike, understanding the value and function of cloud backup servers is essential to ensure data resilience and operational continuity.
This article provides an in-depth exploration of cloud backup servers, explaining their functionality, benefits, challenges, use cases, and future trends.
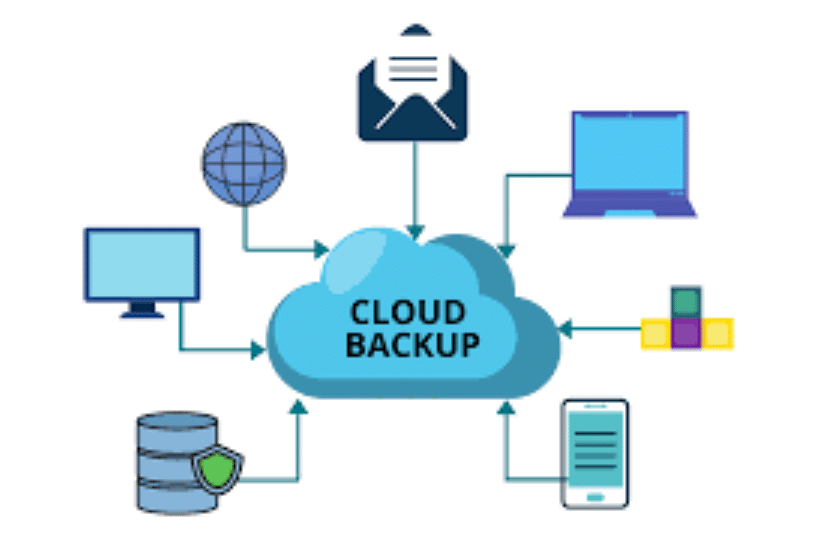
What is a Cloud Backup Server?
A cloud backup server is a remote server used to store digital data over the internet. Unlike traditional backup methods that rely on physical storage devices such as external hard drives or tape systems, cloud backup allows users to automatically upload and store data on a secure, off-site server maintained by a third-party provider.
These servers are hosted in data centers that feature advanced infrastructure for power supply, cooling, security, and disaster recovery. Data is typically encrypted before being transmitted and stored to ensure its confidentiality and integrity.
How Cloud Backup Works
Cloud backup works through a process known as data replication or synchronization, which typically includes the following steps:
-
Data Selection: Users select files, folders, databases, or entire systems to back up.
-
Encryption: Data is encrypted locally using secure algorithms such as AES-256.
-
Transfer: Encrypted data is transmitted to a cloud server via a secure internet connection.
-
Storage: Data is stored in a remote server, often across multiple locations for redundancy.
-
Access and Recovery: Users can restore their data at any time by logging into their account and downloading the files.
Cloud backups can be full, incremental, or differential, depending on the needs and frequency of data changes.
Key Benefits of Cloud Backup Servers
1. Data Security and Encryption
Cloud backup providers use high-level encryption both in transit and at rest, which helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or cyberattacks.
2. Scalability
Unlike traditional methods, cloud servers can scale storage capacity almost infinitely. As your data grows, you can expand your backup space without investing in new hardware.
3. Automation
Backup processes can be automated, reducing human error and ensuring that data is regularly saved without manual intervention.
4. Disaster Recovery
In the event of data loss due to hardware failure, ransomware attacks, or natural disasters, cloud backups provide a reliable recovery solution.
5. Remote Accessibility
Data stored in the cloud can be accessed from any location with an internet connection, which is especially beneficial for remote teams and mobile workforces.
6. Cost Efficiency
While there are subscription fees, cloud backup removes the need for expensive hardware, maintenance, and physical storage space.
Common Use Cases
1. Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs)
Many SMBs use cloud backup servers as a low-cost, efficient way to secure customer data, financial records, and operational documents.
2. Enterprises
Large companies integrate cloud backup into their IT strategies to support compliance, data governance, and risk management.
3. Individual Users
From freelance professionals to students, individuals use cloud backups to protect personal photos, documents, and important files.
4. Government and Healthcare
Regulated industries benefit from cloud backups that offer compliance with standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and ISO certifications.
Types of Cloud Backup Services
Cloud backup services can be categorized into several types based on their infrastructure and target users:
1. Public Cloud Backup
These services are offered by third-party providers such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure. Users share resources in a multi-tenant environment.
2. Private Cloud Backup
Used by organizations with specific security needs, private clouds are dedicated environments not shared with other users, providing enhanced control.
3. Hybrid Cloud Backup
Combining public and private solutions, hybrid backups allow businesses to keep sensitive data in a private cloud while using public storage for less critical files.
4. Managed Backup Services
These involve outsourcing backup management to a service provider who handles configuration, monitoring, and maintenance.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, cloud backup servers also come with challenges that need to be carefully considered:
1. Internet Dependency
Access to cloud backups relies on internet connectivity. A slow or interrupted connection can delay data restoration.
2. Cost Over Time
Although initial costs are low, long-term subscription fees and increased data usage can become costly.
3. Data Privacy Concerns
Storing data on third-party servers raises concerns about privacy, especially in industries handling sensitive information.
4. Compliance Issues
Different countries have varying data protection laws. Organizations must ensure that their cloud provider complies with relevant regulations.
5. Vendor Lock-In
Migrating data from one provider to another can be difficult and expensive, leading to vendor lock-in.
Best Practices for Cloud Backup
To get the most from cloud backup services, it’s important to follow certain best practices:
-
Choose a Trusted Provider: Evaluate providers based on uptime, security certifications, and customer reviews.
-
Implement a Backup Schedule: Use automated, regular backups to ensure data consistency.
-
Use Encryption: Always encrypt data before uploading and ensure the provider supports encryption at rest.
-
Test Restorations: Periodically test the recovery process to ensure backups are reliable and complete.
-
Monitor Usage and Costs: Keep track of storage usage and optimize plans to avoid unexpected charges.
The Future of Cloud Backup
Cloud backup is continuously evolving. With the growth of AI, machine learning, and edge computing, the future promises even more intelligent and efficient backup systems. Some upcoming trends include:
-
AI-Powered Backup Management: Predictive algorithms that determine optimal backup schedules and detect anomalies.
-
Zero-Trust Security Models: Increasing adoption of zero-trust architectures that ensure every access point is verified.
-
Decentralized Storage Networks (DSNs): Peer-to-peer storage networks that offer redundancy and security without centralized control.
-
Integration with DevOps: Cloud backups becoming a key component of CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure-as-code environments.
-
Sustainability Focus: Data centers using green energy and optimizing workloads to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
Cloud backup servers have become indispensable in modern IT strategies, offering an effective and scalable way to protect digital assets. Whether for individual users, small businesses, or large enterprises, the flexibility, security, and convenience of cloud backup make it a top choice for data protection.
However, as with any technology, it’s crucial to stay informed, choose the right solutions, and implement robust practices to maximize benefits and minimize risks. In an era where data is not just valuable but vital, investing in reliable cloud backup is no longer optional—it’s a necessity.
